
$ sudo dd if=/Users/kyle/Downloads/Linux.iso of=/dev/disk2 bs=8m The "unmountDisk" command is used to unmount all volumes of the given disk drive but will keep the drive itself visible to the computer (instead of the eject option that disconnects it entirely). In this case, we are going to assume our flash drive is disk2. For our purposes, we only care about the drive. Volumes are labeled disk1s0, disk1s1, disk1s2, etc. Drives are labeled as disk0, disk1, disk2, etc.
ISO BOOTABLE USB FOR MAC DRIVERS
This command is used to list out all disk drivers and their volumes. STEP 1: Create disk image with dd command
ISO BOOTABLE USB FOR MAC ISO
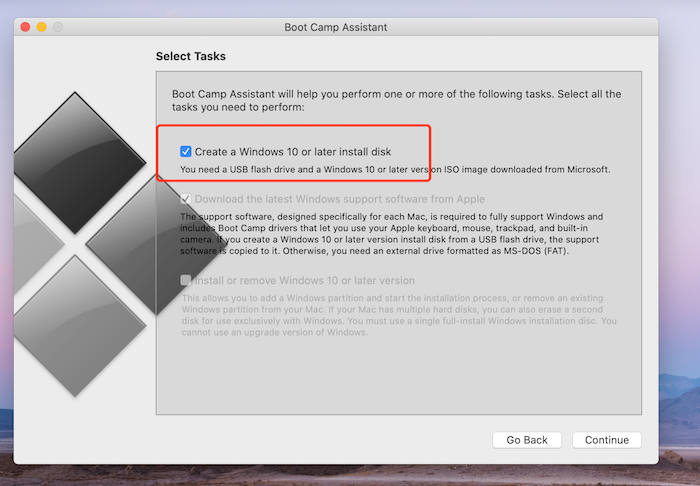
The steps to create a bootable USB from an ISO using dd command are as follows: Here is a list of some basic requirements before we start the process: Note: You'll need to be an administrator to do this.īASIC REQUIREMENTS FOR CREATING A BOOTABLE USB Here are the terminal commands in order, followed by explanations of what they do: ISO file, with no 3rd party apps required. (Linux anyone?) Here is a quick and easy way to make a bootable USB from a.

ISO file is a widely used disk image format and the standard format for bootable media. The command used for this process is:ĭd if=/dev/cdrom of=tgservice.iso bs=2048 ISO file from a source file once the CD is inserted. Create CD ROM backup dd command can create an. Restore using the hard disk dd command can restore a hard disk containing the image file of another hard disk.
Create an image of a hard disk dd command can create an image file of the hard disk and save it on other storage devices. Backup a partition dd command can back up a partition if we specify the partition in the input file, and the output file can be the target path or image file. Backup the entire hard disk dd command can back up an entire copy of a hard disk to another hard disk connected to the same system. Some of the most common uses of the dd command are:ġ. conv - This option is used so that the process of copying continues even if there are any read errors. count - This option is used to specify the number of blocks to be copied (by default, the dd command copies the entire file or disk)ĥ. bs - This option is used to specify the block size, i.e., number of bytes or kilobytes(k) or megabytes(m)Ĥ. if - This option is used to specify an output file or deviceģ. If - This option is used to specify an input file or deviceĢ. The basic dd command syntax consists of the following:ġ. By default, the dd command reads from stdin and writes to stdout these can be modified using its input file and output file options. The dd command's syntax differs from various other Unix programs, as it uses syntax option=value rather than the standard syntax -option value or -option=value formats. Dd is a command-line utility for Linux and Unix systems whose primary purpose is to convert and create low-level file copy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
